Virtual instruments are software-based emulations of real instruments or entirely synthetic sounds that can be used to enhance music production. They offer incredible flexibility, sound quality, and creative potential, making them an integral part of modern music production.
Cubase 12 excels in its virtual instrument support, offering a wide range of features and capabilities to accommodate musicians’ and producers’ needs. Here are some key aspects that make Cubase 12 stand out in this regard:
- VST Instrument Integration: Cubase has long been known for its robust support for VST (Virtual Studio Technology) instruments. VST is an industry-standard plug-in format developed by Steinberg (the company behind Cubase) that allows seamless integration of virtual instruments into the DAW. Cubase 12 continues to refine and expand its support for VST instruments, providing a smooth and efficient workflow for users.
- Expanded Library of Included Virtual Instruments: With each new iteration, Cubase enhances its stock library of virtual instruments. Cubase 12 comes with an extensive collection of high-quality instrument plugins, including virtual synthesizers, pianos, drums, guitars, orchestral instruments, and more. This allows users to start producing right away without needing to invest in additional third-party virtual instruments.
- Sampler Track and Key Editor Enhancements: Cubase 12 introduces improvements to the Sampler Track and Key Editor, making it easier to work with sampled sounds and MIDI data. The Sampler Track enables users to quickly drag and drop audio samples from the MediaBay or directly from their project, turning them into playable instruments. The Key Editor provides enhanced tools for MIDI manipulation and expression, allowing for precise control over virtual instruments’ nuances and articulations.
- Expression Maps and Articulation Control: Cubase 12 enhances expression maps and articulation control, making it easier to work with multi-sampled virtual instruments that feature different articulations. Users can now switch between various playing styles, techniques, or articulations seamlessly within a single MIDI part, resulting in more realistic and dynamic performances.
- Lower Latency and Performance Optimization: Virtual instruments can be demanding on system resources, potentially leading to latency and performance issues. Cubase 12 focuses on optimizing performance and minimizing latency, allowing users to run multiple instances of virtual instruments smoothly and efficiently.
- Improved Compatibility with Third-party Virtual Instruments: While Cubase includes an excellent selection of virtual instruments, many users prefer to expand their collection with third-party plugins. Cubase 12 continues to refine its compatibility with a wide range of third-party virtual instruments, ensuring a seamless integration experience.
In summary, Cubase 12 reaffirms its position as a leading DAW with its robust support for virtual instruments. Its dedication to enhancing the user experience and optimizing performance makes it an excellent choice for musicians and producers seeking a powerful and feature-rich platform to bring their creative ideas to life. As technology evolves and music production techniques advance, Cubase remains at the forefront, offering innovative solutions to meet the needs of the modern music industry.
Types of Virtual Instruments in Cubase 12
Cubase 12, as a leading Digital Audio Workstation (DAW), boasts a diverse range of virtual instruments to cater to musicians and producers’ creative needs. These virtual instruments are software-based emulations of real instruments or entirely synthetic sounds, enabling users to compose, arrange, and produce music with great flexibility and high-quality sounds. Here are some of the main types of virtual instruments available in Cubase 12:
- Virtual Synthesizers:
- Analog Synths: These virtual instruments emulate classic analog synthesizers, delivering warm and rich sounds reminiscent of vintage hardware synths. They are excellent for creating fat basslines, lush pads, and soaring leads.
- Digital Synths: Cubase 12 features digital synthesizers that provide a wide range of modern and futuristic sounds. From crystal-clear plucks to complex evolving textures, digital synths offer plenty of sonic possibilities.
- Sample-based Instruments:
- Virtual Pianos: Cubase 12 includes high-quality sampled pianos, capturing the nuances of acoustic grand and upright pianos. These instruments are perfect for adding realistic piano parts to your compositions.
- Orchestral Instruments: The DAW offers a selection of orchestral sample libraries that cover a broad spectrum of orchestral instruments, such as strings, woodwinds, brass, and percussion. Composers and arrangers can use these virtual instruments to create symphonic arrangements.
- Drums and Percussion: Virtual drum kits and percussion instruments provide realistic drum sounds, making it easy to produce professional-quality drum tracks without the need for recording physical drum kits.
- Drum Machines:
- Classic Drum Machines: Cubase 12 may include virtual versions of iconic drum machines, such as the Roland TR-808, TR-909, or LinnDrum. These instruments are ideal for crafting classic drum machine beats and electronic rhythms.
- Sample Manipulation Instruments:
- Samplers: Cubase 12 incorporates advanced samplers that allow users to import and manipulate their audio samples. With features like time-stretching, pitch-shifting, and slicing, samplers enable creative sound design and exploration.
- Virtual Guitars and Basses:
- Electric Guitars: Virtual electric guitar instruments emulate the sound and playing techniques of electric guitars, enabling users to create authentic guitar parts without needing to record live guitar tracks.
- Bass Guitars: Similarly, virtual bass guitar instruments offer realistic bass sounds and playing styles, perfect for adding low-end grooves to your music.
- Synthesis and Sound Design Tools:
- Modular Synthesis: Cubase 12 might include virtual modular synthesizers, allowing users to create complex and unique sounds by patching modules together in a virtual environment.
- Sound Design Tools: Some virtual instruments may be dedicated to sound design, offering various synthesis methods, effects, and modulation capabilities to sculpt entirely new and innovative sounds.
These are just some of the types of virtual instruments you can find in Cubase 12. The DAW’s comprehensive library and compatibility with third-party virtual instruments ensure that musicians and producers have access to a vast array of sounds and creative tools to bring their musical ideas to life.
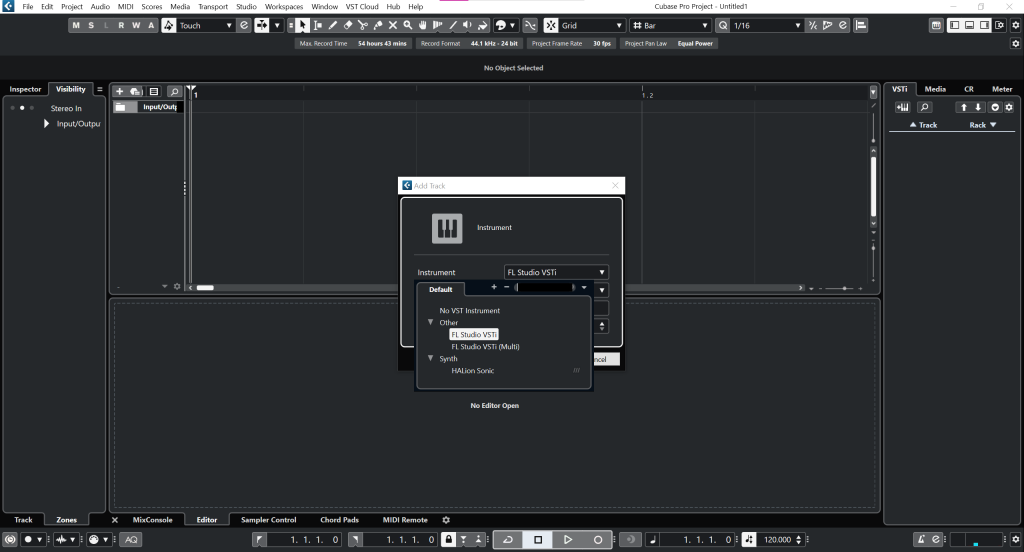
Integrating Virtual Instruments in Cubase 12
Integrating virtual instruments in Cubase 12 is a seamless and straightforward process, thanks to the DAW’s robust support for Virtual Studio Technology (VST) instruments. Whether you’re using Cubase’s built-in virtual instruments or third-party plugins, the integration process is relatively consistent. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to integrate virtual instruments in Cubase 12:
- Installing Virtual Instruments: Before you can integrate a virtual instrument into Cubase 12, you need to install the plugin on your computer. Most virtual instruments come with an installer that places the necessary files in the correct location on your system. Follow the installation instructions provided by the virtual instrument manufacturer.
- Plugin Manager: Once the virtual instrument is installed, open Cubase 12. In the top menu, navigate to “Studio” and select “Plugin Manager.” The Plugin Manager window will appear, showing a list of all available VST instruments on your system.
- Activating Plugins: In the Plugin Manager, make sure the virtual instrument you want to use is listed and has its status set to “Active.” If the instrument is not active, click the checkbox next to its name to activate it. Cubase will then scan the plugin and add it to the list of available instruments.
- Instrument Tracks: To create a track for your virtual instrument, go to the track list on the left side of the Cubase window and click the “+” button. From the dropdown menu, choose “Instrument” to create an Instrument Track.
- Selecting the Virtual Instrument: After creating the Instrument Track, a new window will appear, displaying the available virtual instruments. Browse through the list and select the virtual instrument you want to use. Click “Add Track” or “Create” to finalize the selection.
- MIDI Connections: For the virtual instrument to receive MIDI input, make sure your MIDI controller or MIDI keyboard is connected to your computer and recognized by Cubase. You can set up MIDI connections in the “Studio” menu by selecting “Studio Setup” and then “MIDI Port Setup.”
- Recording and Playing: Now that your virtual instrument is integrated, you can start recording and playing it. To record MIDI data, arm the Instrument Track for recording by clicking the “R” button. You can draw in MIDI notes manually or play your MIDI controller to record your performance.
- Editing MIDI Data: After recording or inputting MIDI data, you can use the built-in MIDI editor in Cubase 12 (the Key Editor) to fine-tune and edit your performance. This editor allows you to adjust note lengths, velocities, and more, offering detailed control over your virtual instrument’s expression.
- Mixing and Processing: Once you have recorded and edited your virtual instrument parts, you can further enhance the sound using Cubase’s extensive range of audio effects and processing tools. Add EQ, compression, reverb, and other effects to shape the sound to your liking.
By following these steps, you can seamlessly integrate virtual instruments into your Cubase 12 projects, unlocking a world of creative possibilities in music production. Cubase’s user-friendly interface and comprehensive features ensure that you can focus on making music without getting bogged down by technical complexities.
Cubase 12 Native Virtual Instruments
- HALion Sonic SE: HALion Sonic SE is a powerful workstation synthesizer that offers a wide range of high-quality sounds across various genres. It includes a vast library of presets, covering pianos, strings, brass, drums, synthesizers, and more. With an intuitive interface, HALion Sonic SE makes it easy to find the right sound for your project.
- Groove Agent SE: Groove Agent SE is a virtual drum machine and beat production instrument. It comes with a collection of drum kits and patterns, suitable for various music styles. The built-in pattern sequencer and extensive editing options allow users to create dynamic and engaging drum tracks.
- Prologue: Prologue is a subtractive synthesizer that produces classic analog synth sounds. It offers a rich set of features, including two oscillators, a filter section, modulation sources, and effects. Prologue is ideal for crafting warm pads, lead sounds, and evolving textures.
- Mystic: Mystic is a unique virtual synthesizer that combines subtractive synthesis with physical modeling. This allows for the creation of organic and expressive sounds that blend the best of both synthesis worlds. Mystic is often used to add ethereal and otherworldly textures to music.
- Padshop: Padshop is a granular synthesizer that excels at creating atmospheric and evolving pads, soundscapes, and textures. Its granular engine allows for the manipulation of audio samples in real-time, resulting in captivating and immersive sounds.
- Retrologue: As the name suggests, Retrologue specializes in producing vintage and retro synth sounds. It features classic oscillator waveforms, filters, and modulation options, making it a go-to choice for classic synth enthusiasts.
- LoopMash: LoopMash is a creative loop-based instrument that allows users to combine and manipulate loops in real-time. It’s a fun tool for experimenting with loops and creating unique rhythmic patterns.
These are just some examples of the native virtual instruments that might be available in Cubase 12. The software’s continuous development ensures that it stays at the cutting edge of music production, providing musicians and producers with an extensive array of virtual instruments to suit various musical styles and preferences.
Third-Party Virtual Instruments and VSTi Support in Cubase 12
Cubase 12 continues the tradition of strong support for third-party virtual instruments through its comprehensive VSTi (Virtual Studio Technology Instrument) support. VSTi plugins are software-based instruments developed by third-party companies, offering a vast array of sounds and features beyond what is included in the DAW’s native virtual instruments. Cubase’s compatibility with these plugins allows users to expand their sonic palette and access cutting-edge sounds from a wide range of developers. Here’s an overview of third-party virtual instruments and VSTi support in Cubase 12:
- VST3 Compatibility: Cubase 12 supports VST3, the latest version of the VST plugin format. VST3 plugins offer improved performance, efficiency, and stability compared to their predecessors, making them a preferred choice for many developers.
- Installation and Scanning: To use third-party virtual instruments in Cubase 12, you need to install the plugins on your computer. During the installation process, the plugins will be placed in the appropriate VST plugin folder on your system. When you launch Cubase 12, the program will automatically scan these folders for VSTi plugins and make them available for use.
- Managing VST Plugins: In Cubase 12, you can manage third-party VST plugins through the Plugin Manager, accessible from the “Studio” menu. The Plugin Manager allows you to activate or deactivate specific plugins, set plugin paths, and check for updates. It’s also possible to organize your plugins into custom folders for better organization.
- Instrument Tracks for Third-Party Plugins: To use a third-party virtual instrument, you can create an Instrument Track in Cubase 12, as you would with native virtual instruments. After selecting the Instrument Track type, you can choose the third-party VSTi from the list of available plugins.
- MIDI Connection: For your third-party virtual instrument to receive MIDI input, ensure that your MIDI controller or keyboard is connected and recognized by Cubase. You can configure MIDI connections in the “Studio Setup” section.
- Recording and Editing: After integrating a third-party VSTi into an Instrument Track, you can record MIDI data or input it manually using Cubase’s MIDI editor. This editor allows you to fine-tune and edit your performance, just like with native virtual instruments.
- Automation and Expression Maps: Cubase 12’s automation features allow you to control parameters within third-party virtual instruments over time. Additionally, you can create expression maps to manage articulations and playing techniques for more realistic performances with compatible VSTi plugins.
- Mixing and Processing: Once you’ve recorded and edited your third-party VSTi parts, you can apply Cubase’s extensive array of audio effects and processing tools to shape the sound further.
By supporting third-party virtual instruments and the VSTi format, Cubase 12 offers musicians and producers limitless creative potential. The ability to integrate a wide range of plugins ensures that users can explore different soundscapes, genres, and styles, ultimately enhancing the music production experience within the Cubase environment.
Conclusion
Cubase 12 offers a robust and diverse selection of virtual instruments, making it a powerful and versatile tool for music production. With a combination of native virtual instruments and strong support for third-party VSTi plugins, Cubase 12 caters to the creative needs of musicians, producers, and composers across various genres and styles.
The native virtual instruments provided by Cubase 12, such as HALion Sonic SE, Groove Agent SE, Prologue, and others, deliver high-quality sounds and a user-friendly interface that simplifies the music-making process. These instruments cover a wide range of musical elements, from realistic acoustic instruments to synthetic and futuristic sounds.
Furthermore, Cubase 12’s extensive support for third-party virtual instruments opens up a world of possibilities for users, allowing them to access cutting-edge sounds from various developers. VSTi compatibility allows seamless integration of third-party plugins, expanding the sonic palette and enabling musicians to explore new creative avenues.
The integration process for virtual instruments in Cubase 12 is straightforward, with Instrument Tracks facilitating easy recording, editing, and manipulation of MIDI data. Users can take advantage of the MIDI editor and expression maps to fine-tune performances and achieve more realistic and expressive results.
Cubase 12’s commitment to performance optimization ensures smooth operation, even with multiple instances of virtual instruments running simultaneously. This allows users to focus on their creativity without being hindered by technical constraints.
Cubase 12’s virtual instruments, both native and third-party, exemplify the DAW’s dedication to providing a comprehensive and professional music production platform. Whether producing electronic, orchestral, or any other style of music, Cubase 12 empowers musicians and producers to bring their artistic visions to life with an impressive array of sounds and creative tools at their fingertips.